Redux
A predictable state container for JavaScript apps.
It helps you write applications that behave consistently, run in different environments (client, server, and native), and are easy to test.
you can use Redux together with , or with any other view library
Redux is a valuable tool for organising your state
Here are some suggestions on when it makes sense to use Redux:
- You have reasonable amounts of data changing over time
- You need a single source of truth for your state
- You find that keeping all your state in a top-level component is no longer sufficient
PredictableRedux helps you write applications that behave consistently, run in different environments (client, server, and native), and are easy to test.
CentralizedCentralizing your application's state and logic enables powerful capabilities like undo/redo, state persistence, and much more.
DebuggableThe Redux DevTools make it easy to trace when, where, why, and how your application's state changed.
FlexibleRedux works with any UI layer, and has a large ecosystem of addons to fit your needs.
Redux : 3 Principals
1.One Immutable Store: Application state is placed in single immutable store, state can be changed directly having one immutable store its debugging,server rendering, and it makes things like undo and redo.
in redux the only way to change state is making an action.
2.Action Triger Changes:
user may trigger some submit button may trigger some action
3. Reducers Update State:
state changes are handled by true functions these are called reducers.in redux reducers are just function that accept the current state and an action and return a new state.
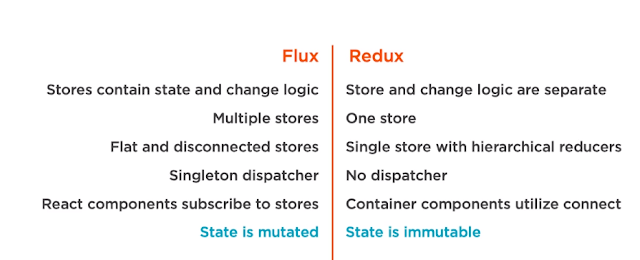
Flux Vs Redux:
flux and redux are two different ways to handle state and data flows in your react application.
both having same unidirectional data flow concept
data flows down action flows up
Similarity-
- Unidirectional Flow
- Action
- stores
Redux new Concepts-
1.Reducer
function that takes current states and actions and then return a new state.
2.Containers-
containers are just react component.used specific .
container component have necessary logics for marshalling data and actions.
3.immutablility
redux storea are immutable
Flux:
when action is triggered store is notified by dispatcher.flux uses singelton dispatcher to connect actions to store.
store use event emitter to connect to the dispatcher.

Redux:
redux doesn't have dispatcher ,redux relies on pure functions called reducers so it doesn't need dispatcher .
pure functions are easy to compose
each action is automatically handled by one or more reducer which update the single store. since state is immutable in redux reducer returns a new updated copy of state which update the store
Action- action describes users intent. that is an object with type property and data.
data portion can be whatever you like. action having type property is mandatory.
Example-
below is the action for course rating , in this you have to rate a course from scale of 1 to 5.
{type: RATE_COURSE,rating:5}
data portion on right (rating ) can be whatever you want ,you can pass multiple seprate peaces of data here or one or more separate object.
Reducer-
This action automatically handled by reducers .reduces is a function that return new state.
it will receive current state and action and return a new state. it typically uses a switch statement that checks type of action this determine new state could be returned.
function appReducer(state=defaultstate,action)
{
switch(action.type)
{
case RATE_COURSE:
//return new state
}
}
as soon as new state is returned from reducer store is updated.react rerender any component that is utilising the data.
Notified via React Redux
new react component is connected with the store using a redux related library called react redux.
Difference between flux and Redux
Action Creators-
in Redux the event happening on application is called actions . actions are just plain objects containing a descriptions of an event.
reateCourse(rating) // Action creator
{
type:RATE_COURSE,
rating: rating //Action
}
Creating Redux Store-
let store= createStore(reducer)
we pass create store function to reducer function ,it work on single responsibility principle store only store data of reducers which will discuss in a moment.handle state changes.
store can
dispatch an action store.dispatch(action)
subscribe to the listener store.subscribe(listener)
return its current state store.getState()
replace reducer replaceReducer(nextReducer)
Immutability :
to change state,return new object
already immutable objects:
Number
String
Boolean
undefiend
null
Mutable
Object
Arrays
Function
Handling Immutable data in JS
1. Ojbect.assign object.assign
creates new object or allow us to specify existing objects as a template.
first parameter is target and then it can accept as many source objects as you want.
Ojbect.assign(target, ...sources)
Example
Object.assign({},state,{role:'admin'});
explanation:
first paramenter is target so it will just create a new empty object.
then it is mixing the new object with existing state.
also changing role property to admin.
2.spread Operator {.....myObj...}
you can also use array,
const newUser =[...states.users]
immutable array .map
methods
(map,filter,reduce)
Handling Arrays:
always prefer - map,filter,reduce,concat,spread
avoid-push,pop,reverse
Action Creators-
in Redux the event happening on application is called actions . actions are just plain objects containing a descriptions of an event.
reateCourse(rating) // Action creator
{
type:RATE_COURSE,
rating: rating //Action
}
Creating Redux Store-
let store= createStore(reducer)
we pass create store function to reducer function ,it work on single responsibility principle store only store data of reducers which will discuss in a moment.handle state changes.
store can
dispatch an action store.dispatch(action)
subscribe to the listener store.subscribe(listener)
return its current state store.getState()
replace reducer replaceReducer(nextReducer)
Immutability :
to change state,return new object
already immutable objects:
Number
String
Boolean
undefiend
null
Mutable
Object
Arrays
Function
Handling Immutable data in JS
1. Ojbect.assign object.assign
creates new object or allow us to specify existing objects as a template.
first parameter is target and then it can accept as many source objects as you want.
Ojbect.assign(target, ...sources)
Example
Object.assign({},state,{role:'admin'});
explanation:
first paramenter is target so it will just create a new empty object.
then it is mixing the new object with existing state.
also changing role property to admin.
2.spread Operator {.....myObj...}
you can also use array,
const newUser =[...states.users]
immutable array .map
methods
(map,filter,reduce)
Handling Arrays:
always prefer - map,filter,reduce,concat,spread
avoid-push,pop,reverse





No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.